In-Situ Soil Testing
In-Depth Geotechnical Inc. has implemented testing procedures for the following in-situ tests:
- Field Vane Shear Test (VST)
- Marchetti Dilatometer (DMT)
- Seismic Dilatometer (SDMT)
- Prebored Pressuremeter Test (PMT) TEXAM UNITS
- Self-boring Pressuremeter Test (SBPMT) Boremac Probe and TEXAM Control Unit
- Slotted Tube Driven Pressuremeter (DPMT)
- Rock Pressuremeter (PRMT) with Probex Unit
- Borehole Shear Test (BST)
- Packer testing for NQ and HQ coreholes
- ko Stepped Blade Test (ko)
In addition, our partnership with In–Situ Soil Testing L.C., from Virginia, in the US, allow us to provide special testing services including Cone Penetration Test (CPTU), k0 Step Blade test, and Rock Borehole Shear Test.
Gallery

Flat Blade Dilatometer (DMT) testing can be used to determine effective horizontal stresses; undrained shear strength (clays) or drained friction angle (sands); preconsolidation pressure; and elastic moduli. When using in combination with seismic accessories (SDMT) we can determine a profile of shear wave velocity with depth.

Test Control unit
The test control unit and the DMT blade. One of the advantages of DMT is the ability to complete sounding in a short period of time, allowing for the collection of substantial amount of data. The main limitation is the presence of cobbles or large rock fragment which will impede the pushing of the blade. In such cases, we pre-drill the hole with our auger rig.
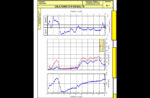
Typical DMT data sheet.
Typical DMT data sheet. This information is used to generate profiles of soil properties and parameters with depth.

Borehole test equipment
Borehole test equipment (BST) can be used to determine drained friction angle of sand deposits, or drained shear strength of clayey soils. This test is the in-situ equivalent of the direct shear test in the laboratory.
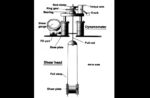
The BST Procedure
The BST procedure consists of applying on the serrated jaws a constant normal stress applied to the borehole wall, while pulling the rods from the surface until shear failure occurs. The shear stress at failure is then determined.

Stress testing
A series of tests under increasing normal stresses is then completed, and a failure envelope can be constructed to determine drained strength parameters. This test is best suited to determined residual strength of soils in failed slopes problems. In such cases, the BST test allows pinpointing the location of a failure surface at depth, and what is the residual strength of the soil required to analyze the slope instability.

Flow and Pressure Testing
Flow and pressure are measured during the test in order to assess permeability, in gal/min or in its grouting equivalent, the lugeon value. At the same time, if flow rates are measured at different pressure levels it is possible to infer rock mass condition for groutability purposes.

3209Pressuremeter Testing
Pressuremeter testing is done on a carefully drilled hole, typically using rotary mud drilling technique. While the procedure is slow, allowing up to 6 tests on a drilling day, the pressuremeter can be used in a wide variety of subsoil conditions, from hard clay till deposits to soft clays, to silt and sand deposits.

Control Unit
Control unit and the pressuremeter probe. During the test two measurements are being recorded: the volume change in the probe and the applied pressure, from which a true stress-strain curve can be plotted. This test determines up to five meaningful parameters related to subsoil conditions: in-situ total horizontal stress (and k0 value); elastic and rebound (unload-reload) moduli; limit pressure (associated to soil’s strength properties); and creep-related properties.

Calibration Procedures #1
One of two calibration procedures completed on a new membrane. In this case, the pressuremeter probe is inflated in the air to obtain the volume-pressure correction curve due to membrane stretching.

Based on the stress-strain test curve, up to five meaningful parameters related to subsoil conditions, i.e., in-situ total horizontal stress (and the associated k0 value); initial elastic modulus; rebound modulus (unload-reload); limit pressure (associated to soil’s strength properties); and creep-related properties.















